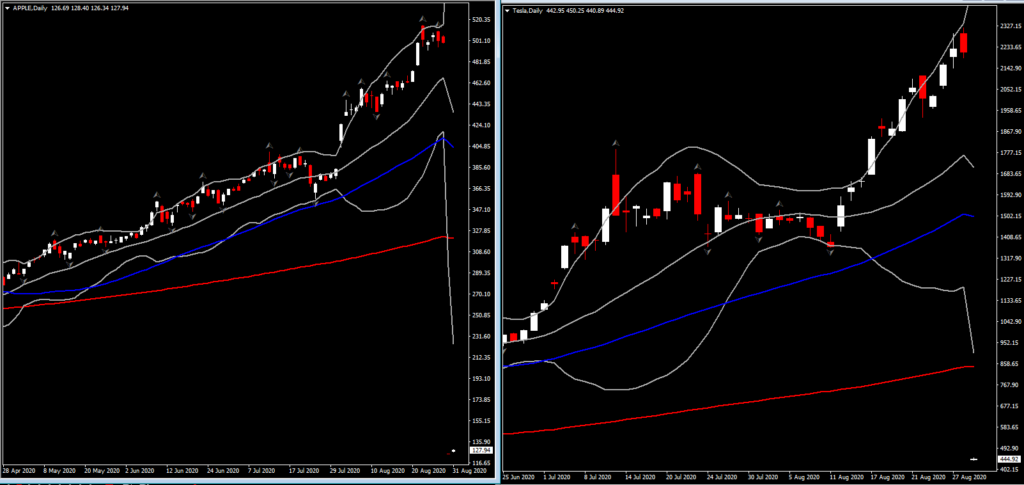
The stock splits of Apple Inc. and Tesla Inc. took effect today. Prior to today’s US session, Apple shares gained more than 1.5% in premarket trading as a 4-for-1 split took effect and Tesla shares added nearly 3% following its 5-for-1 split.
The announcement of stock splits from these giants added fresh momentum to the Wall Street 5-month pandemic rally as generous central bank support helped to keep markets underpinned despite the pandemic, which continues to unfold. Apple’s shares have spiked 33.8% higher since the quarterly earnings report and the split announcement, while Tesla advanced by 66.1% into record highs, as investors cheered the giants’ decision as it was interpreted as an opportunity that theoretically and traditionally increases trading liquidity, retail investing and volume. For Apple an additional contributor in the August rally is also the fact that company surpassed $2 trillion in market cap for the first time ever.
A large part of Apple’s decision is likely due to Apple’s 435% gain since its last stock split back in 2014. At a share price of $514, which has likely become prohibitively expensive for some retail investors, stock splitting has brought Apple’s share price back down to around $124.78. Tesla’s decision on the other hand is likely due to Tesla’s 966% gain in the past year to record highs at $2,280. The Electric Vehicles maker’s shares have been split 5 ways, bringing its share price today back down to around $442.95.
However let’s slip back to the stock split and why it caught so much attention. In general, stock splits by companies in the USA500 faded from prominence after the dot-com bust in 2000, while those by companies in the Dow Jones are even more rare. This is due to the fact that nowadays the benefit of a stock split is far less important now with the ability to trade a single stock or even fractional shares on many stock trading platforms.
Hence tech giants like Apple, Tesla and also Amazon bringing stock splits back into fashion after the massive growth in their shares raises concerns over whether more companies will try to imitate this technique.
What is a stock split?
All public companies have a set number of shares that are outstanding. A stock split is an increase of share number from the company by issuing additional shares, after a company’s board of director ruling. If a company announces a 4-for-1 stock split, the company will give existing shareholders three additional shares for every initial share that they had. For example, if a company had 10 million shares outstanding before the split, it will have 40 million shares outstanding after a 4-for-1 split. Meanwhile the price of the original share will be divided respectively, i.e. if it was worth $100 prior to the splitting, it would trade at $25 after it. Hence as the number of outstanding shares increases, the price decreases but the company’s market value remains constant. The divided should stay steady as well however this is upon the board’s discretion.
Such actions aim to make a company’s share more affordable to retail investors, which will eventually increase liquidity in the stock.
Does it affect the company?
Not really, as the company’s market value remains constant. Other than the lower stock price and traditionally a pop in the price, it means nearly nothing for the company.
What does this mean for the stock market?
Based on The Wall Street Journal research, traditionally Stocks in the USA500 rise 5% in the year following share splits, including 2.5% immediately following the announcement, according to research from Nasdaq Inc. on splits between 2012 and 2018.
As stated earlier, this year things are slightly different, as the announcements managed to boost the relevant companies’ stocks extremely higher. It has been widely mentioned that the outsized reactions to those splits reflect factors including a psychological component with investors embracing tech idols (i.e. FAANGs plus Tesla) during a dismal year full of uncertainties and risks.
Generally however a stock split does not affect the broader stock market, with the Dow Jones Industrial Average being an exception since its value is not weighted by its components’ market value, but from its components’ share price value since it is a price-weighted index. The higher the share price, the bigger the influence that stock has over the Dow’s daily price swings.
Click here to access the Economic Calendar
Andria Pichidi
Market Analyst
Disclaimer: This material is provided as a general marketing communication for information purposes only and does not constitute an independent investment research. Nothing in this communication contains, or should be considered as containing, an investment advice or an investment recommendation or a solicitation for the purpose of buying or selling of any financial instrument. All information provided is gathered from reputable sources and any information containing an indication of past performance is not a guarantee or reliable indicator of future performance. Users acknowledge that any investment in Leveraged Products is characterized by a certain degree of uncertainty and that any investment of this nature involves a high level of risk for which the users are solely responsible and liable. We assume no liability for any loss arising from any investment made based on the information provided in this communication. This communication must not be reproduced or further distributed without our prior written permission.